Amino Acid Chiral Circular Dichroism
Amino acids exhibit optical activity due to the presence of a chiral center on the α-carbon. The two isomers of chiral amino acids are L-type and D-type. Most amino acids in naturally occurring proteins are L-type. Because these amino acids are optically active, they interact with plane-polarized light, leading to the rotation of polarized light.
Circular dichroism (CD) is a spectroscopic technique used to study the optical activity of biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. The technique primarily focuses on how molecules absorb left-handed and right-handed circularly polarized light.
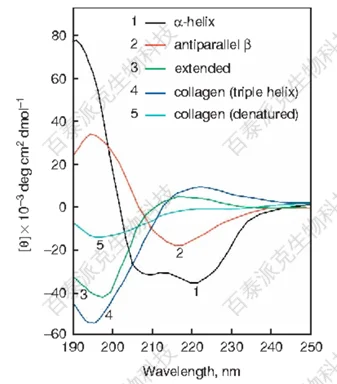
Figure 1
For amino acids and proteins, CD spectra can provide us with the following information:
1. Secondary structure of proteins:
CD spectra can help determine the relative content of α-helix, β-sheet, β-turn, and random coil structures.
2. Structural changes in proteins:
Under changing conditions (such as temperature, pH, or ligand binding), the CD spectrum of a protein may change, reflecting changes in its structure.
3. Chiral identification of amino acids:
CD can be used to identify the relative content of L-type and D-type isomers in amino acid samples.
4. Protein stability:
By measuring CD spectra at different temperatures, the melting temperature of a protein can be estimated, providing insight into its stability.
5. Protein-ligand interactions:
Certain small molecules or other biomolecules may cause structural changes in proteins when they bind, and these changes can be detected through CD spectra.
The advantage of circular dichroism is that it is very suitable for addressing issues related to protein structure and dynamics. However, to obtain quantitative information, more complex data analysis is usually required, and other techniques such as X-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance may be needed to obtain more complete structural information.
Bio-Techne — A leading provider of bioproduct characterization and multi-omics mass spectrometry services
Related services:
Circular Dichroism Analysis (CD)
Protein Structure Identification
How to order?






