Comparison of Five Strategies for Efficient Enrichment of Phosphopeptides (IMAC/TiO₂, etc.)
As one of the most common post-translational modifications, protein phosphorylation plays a central role in biological processes such as signal transduction, cell cycle, and apoptosis. Due to the typically low abundance (<1%) of phosphopeptides in complex proteomes, direct LC-MS/MS analysis is challenging for comprehensive coverage. Therefore, effective phosphopeptide enrichment before mass spectrometry analysis becomes a crucial step in uncovering phosphorylation modification networks.
1. IMAC (Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography)
1. Principle and Mechanism
IMAC utilizes immobilized metal ions (such as Fe³⁺, Ga³⁺) to selectively bind phosphopeptides through electrostatic interactions with phosphate groups.
2. Advantages
-
High enrichment efficiency for multi-phosphopeptides;
-
Mature method, compatible with various pretreatment workflows;
-
Can be reused, relatively low cost.
3. Disadvantages
-
Tends to co-enrich peptides containing acidic amino acids (such as Asp/Glu), reducing specificity;
-
Slightly lower selectivity for mono-phosphopeptides.
2. TiO₂ (Titanium Dioxide Chromatography)
1. Principle and Mechanism
The surface of TiO₂ has a phosphate-affinity nature, selectively binding phosphopeptides through Lewis acid-base interactions.
2. Advantages
-
Higher specificity, especially suitable for enriching low-abundance phosphopeptides;
-
Easy to operate, adaptable to various buffer systems.
3. Disadvantages
-
Tends to co-enrich negatively charged non-phosphopeptides (such as acidic polypeptides);
-
Preference for mono-phosphopeptides, multi-phosphopeptides may not elute completely.
3. ZrO₂ (Zirconium Dioxide Chromatography)
1. Principle and Mechanism
ZrO₂ also acts as a Lewis acid carrier but has a stronger affinity for phosphate groups, especially suitable for operation under neutral pH conditions.
2. Advantages
-
Better than TiO₂ at avoiding co-enrichment of acidic peptide segments;
-
Better retention capacity for multi-phosphopeptides compared to TiO₂.
3. Disadvantages
-
Relatively high cost, limited use at industrial scale;
-
Enrichment conditions are more sensitive to buffer composition.
4. MOAC (Metal Oxide Affinity Chromatography)
1. Principle and Mechanism
MOAC is a broad term that includes various metal oxide carriers like TiO₂ and ZrO₂, achieving selective enrichment through interactions between phosphate groups and metal centers.
2. Advantages
-
Flexible material choice based on research goals;
-
Complementary to IMAC, suitable for tandem enrichment strategies.
3. Disadvantages
-
Sensitivity to sample types varies with different oxides, requiring optimization of conditions;
-
Reliant on material stability and batch-to-batch consistency.
5. Phospho-specific Antibody Enrichment
1. Principle and Mechanism
Uses monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies specific for certain sites or modification forms (such as p-Tyr, p-Ser, p-Thr), capturing phosphopeptides through immuno-enrichment.
2. Advantages
-
Highly specific, suitable for targeted site research;
-
Allows for site-level quantification and tracking.
3. Disadvantages
-
High cost;
-
Cannot comprehensively cover unknown phosphorylation sites;
-
Large batch-to-batch variation in antibodies, affecting reproducibility.
6. Comparative Summary Table
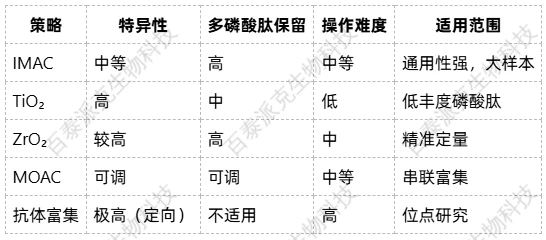
7. Biotech Advantages in Phosphopeptide Research
In phosphoproteomics research, Biotech-Pack utilizes a high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry platform combined with an independently optimized IMAC-TiO₂ tandem enrichment strategy to achieve:
-
Over 30% improvement in phosphopeptide coverage;
-
Detection of over 10,000 phosphorylation sites in a single analysis;
-
Accurate differentiation of Ser/Thr/Tyr modifications, supporting quantitative analysis;
-
Support for multi-species and multi-tissue samples (human, mouse, plants, etc.).
The strategies for phosphopeptide enrichment are diverse, each with its own merits. Researchers should make a reasonable choice based on research objectives, sample type, and budget. Biotech-Pack is committed to transforming cutting-edge technology into efficient research tools to help you accurately analyze phosphorylation regulatory mechanisms.
Biotech-Pack--A premium service provider for bioproduct characterization and multi-omics mass spectrometry analysis.
Related services:
How to order?






