Exploring Biological Structures: Circular Dichroism Experiment
Circular Dichroism (CD) spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique widely used in the structural study of biomolecules, particularly proteins and nucleic acids.
I. Basic Principles:
CD spectroscopy measures the differential absorption of left- and right-circularly polarized light by molecules. This difference is caused by the chirality of the molecules, meaning that they can exist in two mirror-image forms that absorb circularly polarized light differently. Chiral molecules will absorb more light in one rotational direction, resulting in the circular dichroism effect. This property is particularly pronounced in biomolecules like proteins and nucleic acids, which have complex three-dimensional structures and chiral amino acid residues.
II. Experimental Equipment and Procedure:
CD spectrometers typically include a light source, monochromator, sample cell, detector, and data processing system. During a CD scan, circularly polarized light passes through a solution containing the biomolecule of interest. After passing through the sample, the detector measures the absorption of light at different wavelengths. A range of wavelengths is usually measured to construct a spectrum showing the difference in absorption of left- and right-circularly polarized light at various wavelengths.
III. Data Analysis:
CD spectra can provide information about the secondary structure of molecules. For example, the α-helix, β-sheet, and random coil structures in proteins produce characteristic CD signals at specific wavelengths. By comparing with reference spectra of known structures, the approximate secondary structure composition of an unknown sample can be analyzed. CD spectroscopy can also provide information on conformational changes in proteins, such as those induced by temperature, pH, or chemical modifications.
IV. Applications:
1. Protein Folding and Conformational Changes:
CD can be used to study protein folding states under different environmental conditions, which is crucial for understanding protein function and stability.
2. Protein-Ligand Interactions:
By observing CD spectral changes induced by ligand binding, the interactions between proteins and small molecules, drugs, or other proteins can be studied.
3. Protein Engineering and Drug Development:
CD is a very useful tool for examining whether variants in protein engineering or drug candidates in drug development affect binding to target proteins.
4. Nucleic Acid Research:
CD is not limited to proteins and can also be used in the structural study of nucleic acids, aiding in the understanding of DNA and RNA structures and their interactions with proteins and other molecules.
V. Advantages and Limitations:
1. Advantages:
CD spectroscopy requires relatively low sample amounts and can be performed in solution without complex sample preparation. Additionally, as a non-destructive analysis, it is suitable for studying dynamic processes.
2. Limitations:
CD spectroscopy mainly provides information about secondary structures, offering limited insights into the detailed three-dimensional structure of molecules. Detection may also be constrained for molecules without significant secondary structure or at low concentrations.
CD is a powerful tool with significant importance in understanding the structure and function of biomolecules, as well as their interactions and responses to environmental changes.
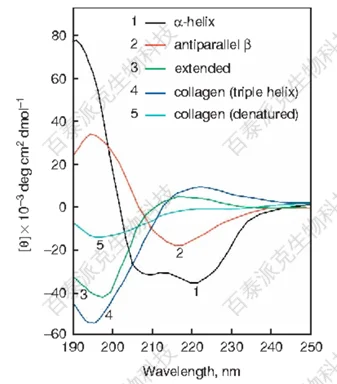
Figure 1
BiotechPack, A Biopharmaceutical Characterization and Multi-Omics Mass Spectrometry (MS) Services Provider
Related Services:
Circular Dichroism Analysis (CD)
Protein Structure Identification
How to order?






